The Significance of Heart Rate Variability in Relation to Food Reward and Energy Expenditure
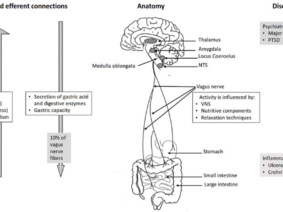
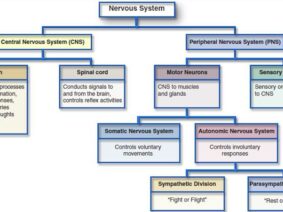
Heart rate variability is a measure of the variation in time between successive heartbeats, and it is an indicator of the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Fasting increases heart-rate variability, while food consumption decreases heart-rate variability. Therefore, heart rate variability is an important physiological marker of the body’s response to food and can be used to assess the effects of interventions such as non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation on food reward and energy expenditure.
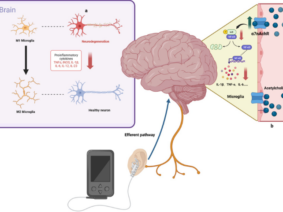
Understanding Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Impact on Nutrition, Weight Management, and Mechanisms Explained
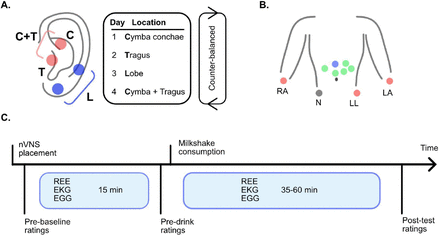
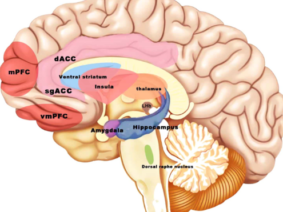
Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) involves the application of electrical stimulation to the auricular branch of the vagus nerve via the skin of the ear. This stimulation is thought to activate the vagus nerve, which plays a key role in regulating food intake, energy expenditure, and metabolism . The potential applications of taVNS in the field of nutrition and weight management include reducing food cravings, decreasing food intake, and increasing energy expenditure . However, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying these effects and to determine the optimal parameters for taVNS stimulation.
Exploring taVNS Applications in Weight Management and Nutrition: Clinical Potential and Usage Insights
In clinical settings, taVNS may be used as an adjunct to other weight management interventions, such as diet and exercise, to enhance their effectiveness. Additionally, taVNS may be useful for individuals who are unable to engage in more strenuous interventions due to physical limitations or other health concerns. However, further research is needed to fully understand the effects of taVNS on human physiology and to determine the optimal parameters for stimulation before it can be widely used in clinical settings.