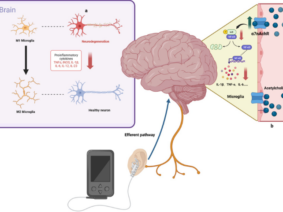
The world of sports and performance recovery has witnessed groundbreaking advancements in recent years. One such innovation gaining attention is Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS). Athletes and researchers alike are intrigued by the potential benefits VNS could offer in aiding post-exertion recovery and enhancing overall sports performance.
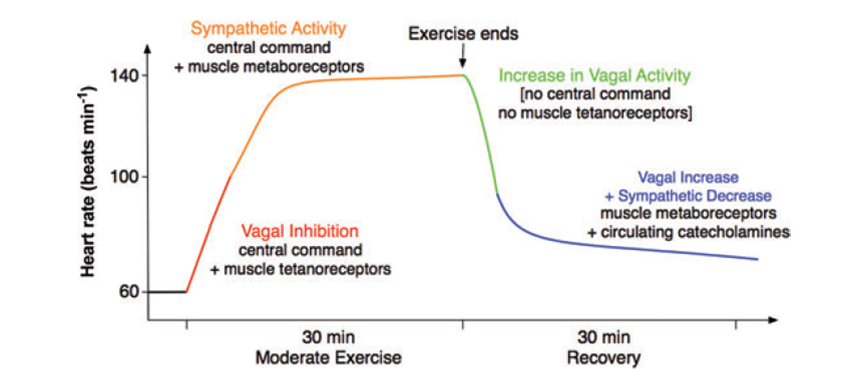
The Impact of Exercise on the Sympathetic Nervous System
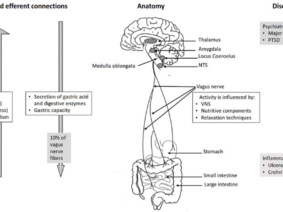
The Vagus Nerve, also known as the “wandering nerve,” plays a significant role in regulating various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. Recent studies have demonstrated its potential impact on recovery after sportive performances.
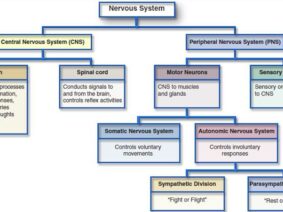
During intense physical activity, the body experiences stress and fatigue, leading to various physiological changes. The activation of the sympathetic nervous system, responsible for the body’s “fight-or-flight” response, occurs during exercise. While this response is crucial for performance, it can also delay recovery as the body remains in an elevated state of arousal.
Here’s where Vagus Nerve Stimulation comes into play. By stimulating the vagus nerve, the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for the “rest-and-digest” response, is activated. This shift towards the parasympathetic state allows the body to enter a state of relaxation and recovery more efficiently.
Promising Results: Studies on VNS with Elite Athletes
A study conducted with elite athletes found that post-training VNS significantly reduced heart rate and cortisol levels, indicating a quicker recovery process. Additionally, athletes reported experiencing reduced muscle soreness and improved sleep quality after VNS treatments.
Convenience and Non-Invasiveness
Vagus Nerve Stimulation is typically administered through a small device that sends gentle electrical pulses to the nerve. Athletes can use this device either immediately after intense workouts or during designated recovery periods. The convenience and non-invasiveness of this approach make it an attractive option for athletes aiming to optimize their recovery strategies.
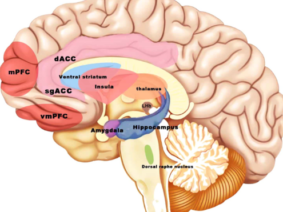
Furthermore, VNS may also benefit athletes by positively impacting their mental and emotional well-being. Sports performance can often lead to stress, anxiety, and even symptoms of overtraining. VNS has been shown to activate brain areas associated with mood regulation, potentially aiding in stress reduction and promoting a more positive mental state.
However, it’s essential to note that while VNS shows promise, it should not replace traditional recovery methods such as proper nutrition, hydration, and rest. Instead, it should be seen as a complementary tool to enhance an athlete’s recovery protocol.
As with any emerging technology, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects and potential risks of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in the context of sports performance recovery. Athletes considering VNS should consult with medical professionals experienced in its application to ensure it aligns with their individual needs and goals.
In conclusion, Vagus Nerve Stimulation presents an exciting avenue for athletes seeking to optimize their recovery after sportive performances. By promoting a shift towards the parasympathetic state, VNS can accelerate the body’s recuperation process, reduce stress levels, and potentially enhance overall sports performance. As research in this area continues, athletes and coaches should keep a close eye on the evolving role of VNS in the world of sports and recovery.